Today it is an era where people give importance to their fitness and wellness. They have realised the importance of quality and comfort in their life. Gone are the days when you had to just sit and suffer from your knee pain and accept it as inevitable while you grow old. Nobody wants to suffer from knee pain and hamper his daily routine activities together with the quality of his life. People want to live life to the fullest. That’s why Total Knee Replacement (TKR) surgery has today become commonly performed and is a highly successful surgical procedure. Recent surgical innovations have resulted in further improvement in its early and long-term surgical outcomes. New implant materials and designs provide a greater and more normal range of motions. Also, a better understanding of the role of the ligaments associated with the knee joint has resulted in improved joint stability and durability.
WHAT IS TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT?
Total Knee Replacement is a surgical procedure that helps to reduce discomfort and restore function in severely damaged knee joints. The operation involves removing defective bone and cartilage from your thigh bone, shinbone, and kneecap and replacing it with a prosthesis made from a variety of materials, including metal alloy or plastic.
Knee replacement surgery was first performed in 1968. Since then, improvements in surgical materials and techniques have greatly increased its results. Total knee replacements are one of the most successful procedures in all medical procedures performed.
WHY IS TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT SURGERY DONE?
The most common reason to perform Total Knee Replacement Surgery is to relieve severe pain and discomfort caused by osteoarthritis and other types of arthritis like rheumatoid arthritis, arthritis after any bone injury (post-traumatic arthritis). For patients who require knee replacement surgery, walking, climbing stairs, standing for a long duration and getting in and out of chairs are all common issues. Even while they are at rest, some people might experience knee pain.
Arthritis is the most common cause of chronic knee pain and impairment. Despite the fact that there are numerous varieties of arthritis, the three most common causes of knee pain are osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and post-traumatic arthritis.
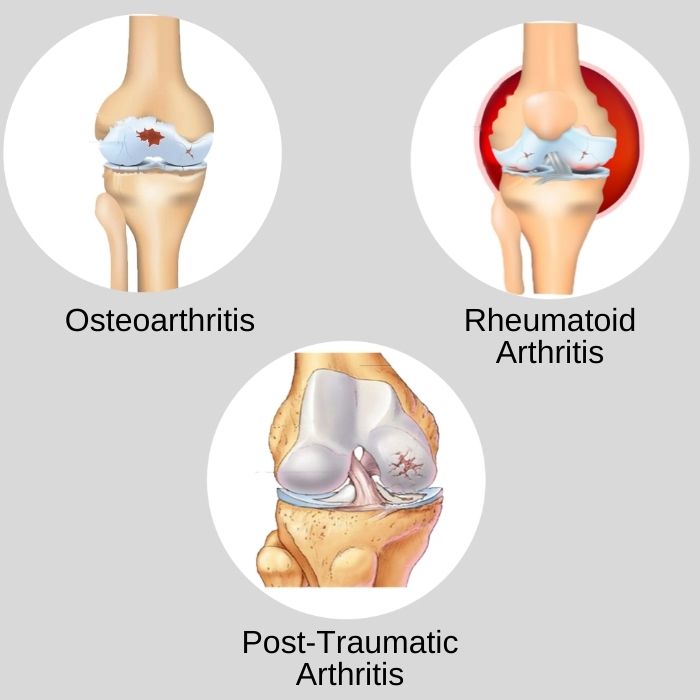
- Osteoarthritis: This is a "wear and tear" type of arthritis that develops with age. It primarily affects those over the age of 50, but younger people can also be affected. The cartilage that cushions the knee's bones weakens and wears away over time. Knee pain and stiffness resulting from the bones rubbing against one another.
- Rheumatoid arthritis: It is a type of inflammatory arthritis that affects the joints. In rheumatoid arthritis, the body's immune system attacks its own tissue, including joints. The synovial membrane that covers the joint becomes inflamed and swollen. It often starts at a young age and is common in young people.
- Post-Traumatic Arthritis: It is caused by a traumatic event. This can happen as a result of a major knee injury. Fractures of the bones surrounding the knee, as well as tears in the knee ligaments, damage the articular cartilage over time, producing pain and limiting function.
WHO IS THE CANDIDATE FOR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT?
Patients whose knee joints have been compromised by degenerative arthritis, trauma, or other rare joint-destructive disorders might undergo total knee replacement surgery.
Whether a person is a good candidate for Total Knee Replacement Surgery is a decision best made by an orthopaedic surgeon. Factors that are taken into consideration include the person's medical history, level of knee pain, and ability to function, along with results of a physical exam, X-rays, and in some cases other tests like a blood test or MRI.
The most important factor to decide whether you should go for a total knee replacement or not is based on the amount of pain and disability experienced by you.
Other factors that make someone a good candidate include the following:
Pain - When pain is severe enough to impact everyday activities, it may be wise to consider surgery. Pain although moderate but which is present even at rest or at night can be another indication.
Inflammation -
